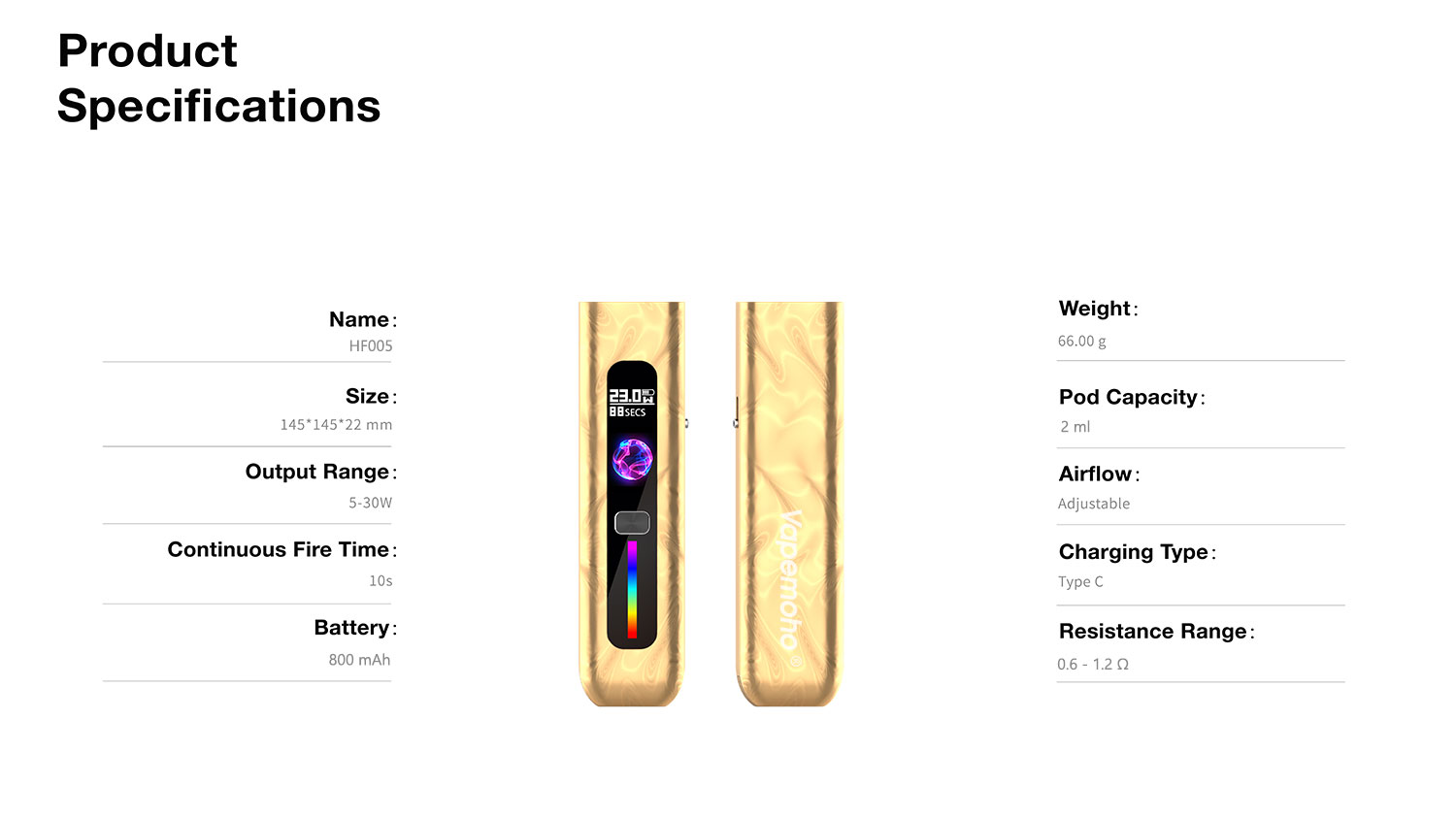
For many consumers and brand partners, an e-cigarette’s journey remains a mystery. It starts with raw materials and ends as a finished product. However, stepping inside a modern e-cig factory reveals a structured process. This process balances precision engineering, strict safety standards, and efficient production. At VAPESKY’s facilities, every step focuses on consistent, compliant, high-performance products. In fact, this rigor sets industry leaders apart from generic manufacturers.
1. Raw Material Inspection & Preparation
To start with, production begins with rigorous raw material screening. VAPESKY sources food-grade plastic for cartridges and medical-grade stainless steel for heating elements. Additionally, we secure pharmaceutical-grade nicotine (where compliant) from vetted suppliers. Our team subjects every material batch to third-party lab tests; specifically, we check for purity and safety. We immediately reject non-compliant materials to avoid compromising subsequent processes.
This strict vetting aligns with VAPESKY’s premium e-cig component supply chain standards, ensuring no subpar materials enter production. Once materials pass inspection, we prepare them for manufacturing: we mold plastic into cartridge shells, cut metal parts to precise dimensions, and mix e-liquids in sealed, temperature-controlled tanks. This tank setup avoids contamination, while all preparation happens in ISO 8 cleanrooms to maintain hygiene and batch consistency. Furthermore, our team monitors cleanroom conditions to prevent external impurities from affecting raw material quality.

2. Core Component Manufacturing
Next, we focus on core component manufacturing—atomizers (heating coils) and batteries—since these parts define an e-cigarette’s performance. VAPESKY uses automated machinery to wind heating coils to exact resistance levels, typically 1.0–1.8 ohms for mouth-to-lung devices. Our technicians test each coil for conductivity before moving it to the next stage; this step reduces defect rates to less than 0.5%. Moreover, automated winding ensures consistent coil quality across all production batches.
We also assemble lithium-ion batteries in dedicated lines and test them for capacity, voltage stability, and safety. Our team subjects every battery to short-circuit and overcharge testing to meet global standards like UL 1642. Notably, component quality is non-negotiable here: faulty batteries or coils cause most e-cig failures, so we never compromise on these critical parts. In addition, we document battery testing data to ensure traceability for regulatory compliance.
3. Assembly & Initial Testing
Moving on to assembly, automated lines bring all components together seamlessly. Precision dispensers fill cartridges with e-liquid to avoid overfilling, while robots attach atomizers to batteries and machines seal mouthpieces onto cartridges. For disposable e-cigarettes, the entire process runs fully automated; one line can produce 50,000 units per day. This efficiency aligns with VAPESKY’s factory production capacity benchmarks and meets high-volume market demands.
After assembly, each device undergoes initial testing: our technicians check vapor output, inspect for leakages, and test button responsiveness. We pull any device that fails this quick check for rework or disposal; only 100% functional units proceed to quality control. As a result, we maintain consistent quality across all production runs, and this initial screening significantly reduces QC workload later.

4. Quality Control & Certification
The QC stage serves as the final checkpoint before packaging. VAPESKY’s QC team samples 5% of each batch for intensive testing: we analyze vapor for harmful byproducts, run durability tests (including drop tests and water resistance checks), and verify compliance with labeling and nicotine content requirements. All tests adhere to VAPESKY’s e-cig quality control standards, which exceed global rules like TPD3 and PMTA. Additionally, random sampling ensures that even small production batches meet the same high standards.
We only award certification labels to passing batches. This stage ensures every outgoing e-cig meets safety, performance, and regulatory standards—critical for building trust with global customers. Without rigorous QC, we couldn’t maintain our reputation for reliability; thus, we never rush or simplify this step. Furthermore, we provide certification documents to clients to support their market entry processes.
5. Final Packaging & Distribution
Finally, certified e-cigarettes move to packaging lines, where we place them in child-resistant packaging—a requirement in most global markets. We customize packaging for regional needs: we add multilingual labels for the EU, include age-verification stickers for the U.S., and print local language warnings for Asia-Pacific. Additionally, we meet regional sustainability standards where applicable, using eco-friendly materials when permitted by regulations. For example, we incorporate recyclable packaging for markets that mandate it.
Once packaged, we palletize products and store them in temperature-controlled warehouses prior to shipping. VAPESKY’s logistics team coordinates with global freight partners to ensure timely delivery to distributors. We also maintain full compliance with customs and import regulations for each target market, preventing delays at border checkpoints. Ultimately, we transform raw materials into fully compliant, ready-to-sell e-cigarettes—proof of the precision that defines modern e-cig manufacturing.